Agtech in Indonesia: Outlook and Promise
(Reference: Indonesia Agritech Report 2020 by A CompassList Research Publication)
Akmal Fauzi - 03 Nov. 2022
Indonesia is a major global producer of several agricultural products and one of the world's top three sources of widely caught and farmed seafood. 9 out of 10 farmers and fishermen live in rural areas and have less access to education, finance, and infrastructure such as drinking water, electricity, and sanitation facilities. Farmers' source of livelihood depends on small-scale farming. However, the agricultural inputs (seed, feed and nutrients) they have access to are sometimes of poor quality.
Likewise, the low-tech traditional farming methods used also cause stagnant and even decreased crop yields. These challenges make Indonesia a promising ground for agritech. Technology helps small farmers and fishermen to produce more efficiently and earn enough income to get out of poverty. It can be concluded that Indonesia has several challenges with agriculture including supply chain inefficiencies, limited access to fair financing, lack of education and agricultural guidance, and the lack of new agricultural technologies.

Agritech in Indonesia can be divided into four based on the business models, namely:
Financing: Startups in this category focus on the lack of access to capital and fair financing requirements for small farmers. Online or peer-to-peer (P2P) crowdfunding platforms attract funds from retail investors, microfinance institutions and banks, funneling money into agriculture. An example of a player in this group is the TaniGroup.
E-commerce: Startups in this category simplify the agricultural supply chain by connecting farmers directly to the final buyers, and in the process eliminate many of the middlemen thereby reducing the trade margins and driving up the final price of goods the farmer receives. As a result, farmers get a fairer selling price and consumers sometimes benefit from a cheaper product in the process. Buyers can become consumers, small businesses and even large-scale producers. Examples of players in this space include: 8 Villages, Aruna and TaniGroup.
Education and Guidance: Startups in this category teach Indonesian farmers and fishermen the skills and knowledge needed to increase productivity. 8 Villages, Aruna and TaniGroup are examples of players in this space
Technology development: Startups in this category such as JALA create new hardware and software that enhances farming operations. These include sensors for collecting farm data, automatic fertilizer or fodder dispensers, drones and VR/AR devices.
In Indonesia alone there are over 131 Agritech Startups. The top 10 most interesting agritech startups are eFishery, TaniHub, Aruna, AgriAku, Eden Farm, Pitik, Crowde, DELOS Aqua, JALA, Semaai. (source: tracxn.com)
In terms of funding or investment, Indonesia agritech has attracted around $33.15 million through seed funding rounds up to Series B since 2013, based on publicly available data. The true figure is likely to be higher because in many rounds of funding, the amount of money raised is not disclosed. The US is the top market for agritech investment in 2019 with several venture capital backed agri and food-tech companies. The second and third places are the two largest countries in Asia, namely China ($3.2 billion) and India ($1.3 billion). . Some investors for agritech Indonesia are East Ventures, Hatch, Salim Group, UMG Idealab Indonesia, Alpha JWC Ventures, Mandiri Capital Indonesia, Telkomsel, Sinar Mas Digital Ventures, Triputra Group, 500 Startups, Brinc. 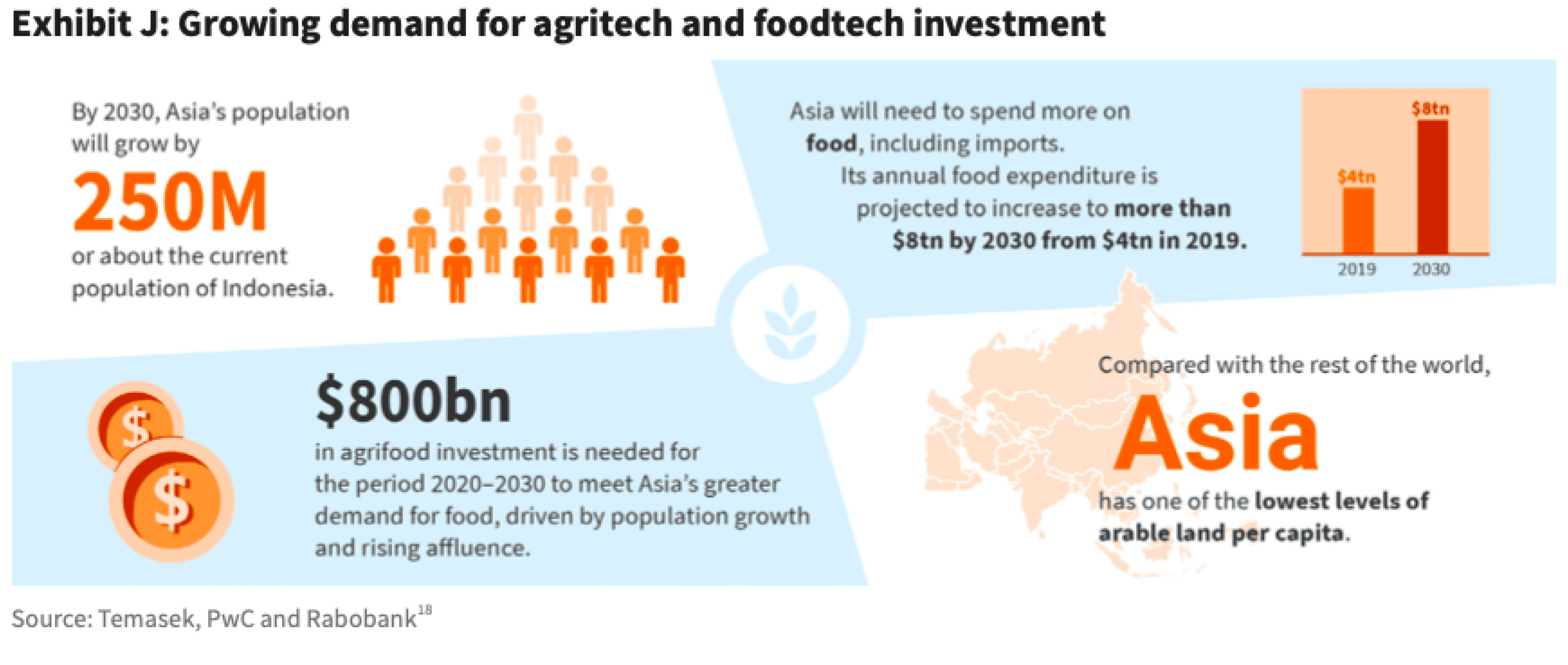
Company
Resources
English
Bahasa
